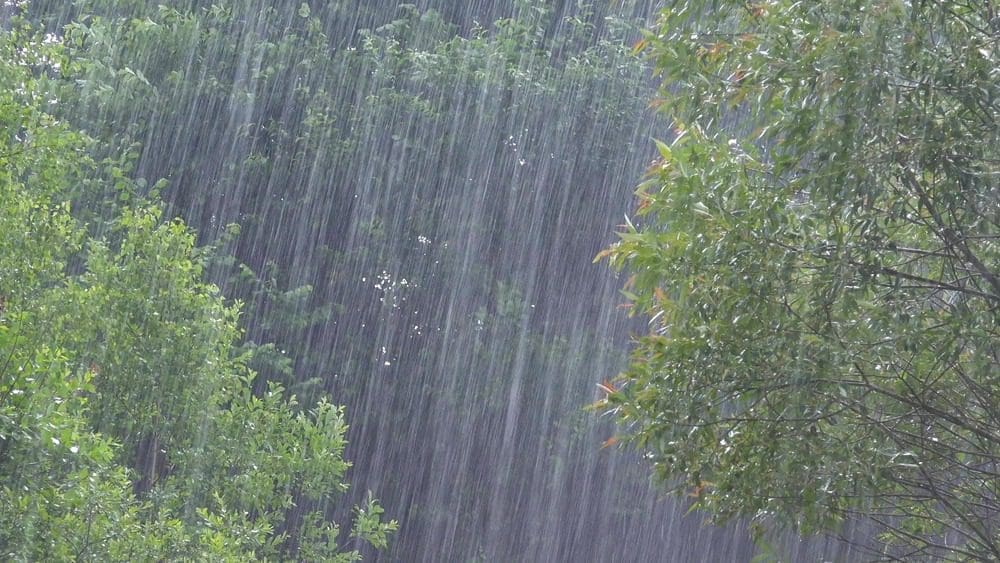
How did four months’ worth of rain fall on the Texas Hill Country in just four hours? From record-breaking Gulf moisture to a stalled storm pinwheel, here are nine science-backed factors that turned a July thunderstorm cluster into one of the deadliest floods in the Lone Star State’s history.
Four Months of Rain in Four Hours
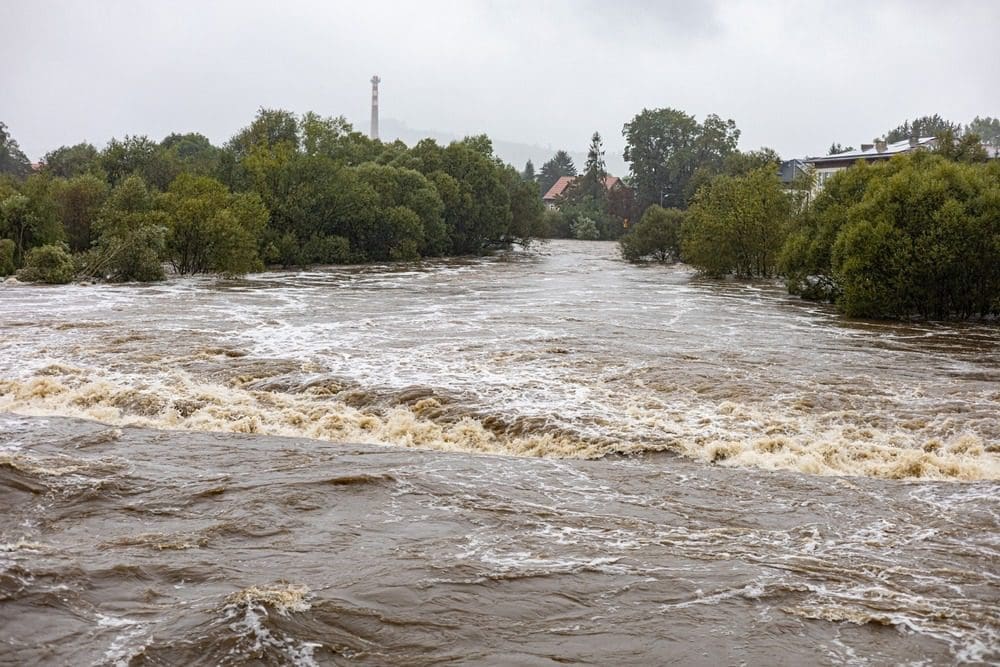

Radar estimates showed 10–15 inches—roughly a season’s average—in a predawn burst over Kerr County, sending the Guadalupe River from 7 ft to 29 ft almost instantly.
Remnant Tropical Moisture Super-Charged the Air

Leftover humidity from dissipated Tropical Storm Barry, plus bath-warm Gulf waters, primed the atmosphere with a deep reservoir of water vapor ready to squeeze out as torrential rain.
A Blocking Ridge Let Storms Park in Place

Upper-level winds were weak, trapped beneath a stagnant high-pressure dome. With no steering flow, thunderstorm cells lingered and re-fired over the same valleys for hours.
“Training” Thunderstorms Repeatedly Hit the Same Track
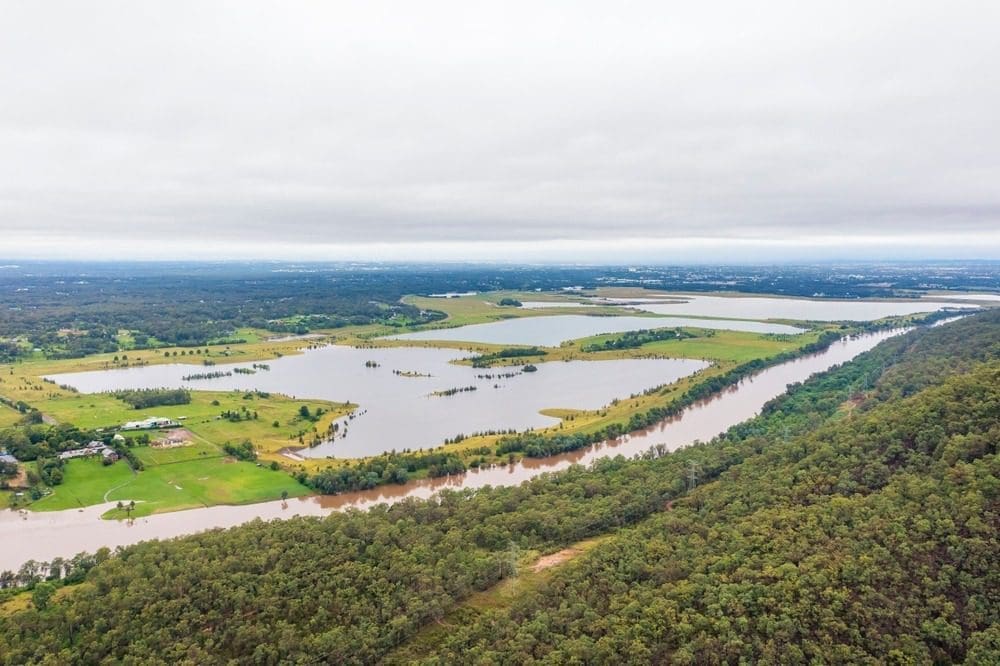

A mesoscale convective vortex acted like a pinwheel, pulling moist air northward and regenerating downpours along a narrow corridor.
Record-High Precipitable Water Values

The column of air above the flood zone held ~2.25 inches of precipitable water—top 0.5% for the region—meaning the atmosphere was nearly wringing wet before storms even fired.
Hill Country Topography Turns Rain into Rapids

Steep limestone hills, thin soil, and narrow canyons funnel runoff straight into rivers, leaving residents mere minutes—not hours—to react when gauges spike.
What a “100-Year Flood” Really Means
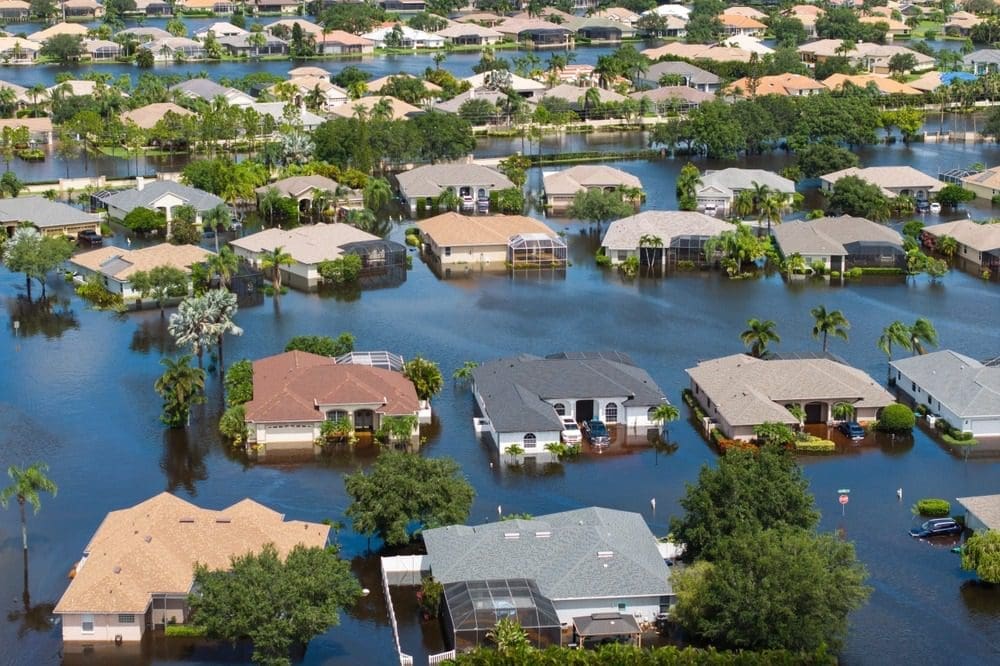

The term denotes a 1-in-100 annual statistical chance at a given location, not a calendar guarantee. Multiple “100-year” floods can occur within a decade if odds collide with changing climate patterns.
Climate Change Is Raising the Ceiling on Extreme Rain

Warmer air holds more moisture, and hotter Gulf waters supply it faster. Scientists note a clear upward trend in Texas’ heaviest downpours even if attributing a single storm takes time.
Nighttime Timing Heightened the Danger

The worst rain struck between midnight and dawn, when most people were asleep and visibility was nil—reducing warning lead time and boosting casualty risk.